The world of electronics heavily relies on a component known as the Switching Power Supply. This technology is fundamental in powering devices from smartphones to industrial machines. According to a recent report by Market Research Future, the global switching power supply market was valued at approximately $20 billion in 2022 and is expected to grow significantly in the coming years.
Industry expert Dr. Emily Chen emphasizes its importance, stating, “Switching Power Supply units are crucial for efficiency and performance.” With their ability to convert electrical power more efficiently than traditional methods, they reduce energy waste. However, challenges remain. Many designs struggle with electromagnetic interference, which can impact device performance.
Moreover, not all switching power supplies are created equal. Some might not meet the latest efficiency standards. This inconsistency calls for careful selection and rigorous testing. Understanding the intricacies of switching power supplies is essential for engineers and manufacturers.
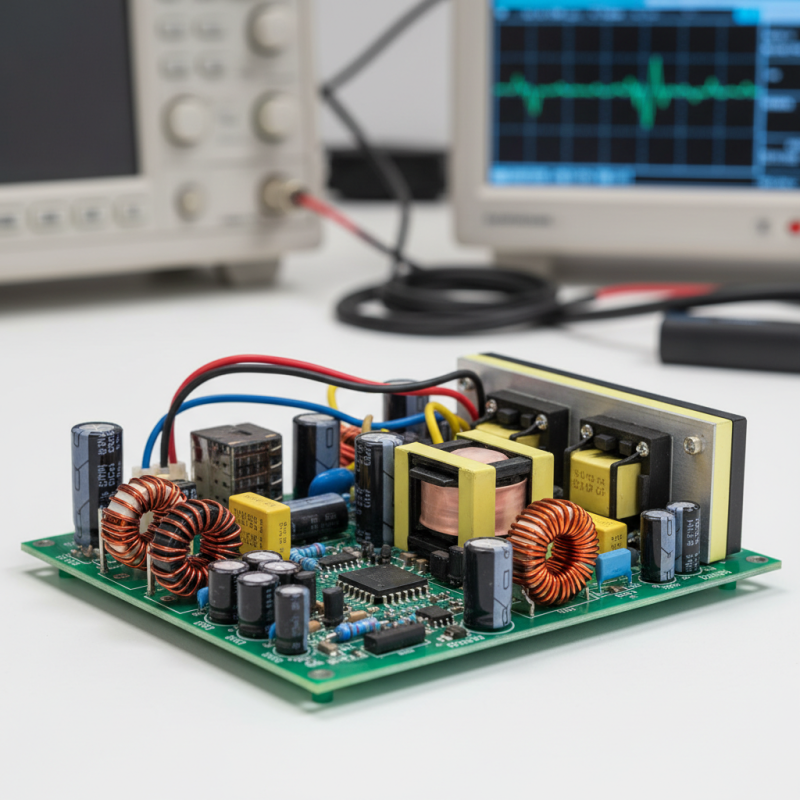
A switching power supply is a type of power supply that converts electrical power efficiently. It’s found in many devices, such as computers and televisions. Unlike linear power supplies, switching power supplies use a high-frequency switching element. This element turns the input voltage on and off quickly. The result is a compact design with less heat generated.
In operation, these power supplies take an input voltage and adjust it to the desired output. They typically include a transformer to modify voltage levels. The switching process creates a control feedback loop that maintains the output voltage. The design offers flexibility, allowing different voltages and currents based on system requirements.
However, switching power supplies are not without challenges.
They can introduce electrical noise into a system. This noise can interfere with other signals. Additionally, achieving a perfect balance between efficiency and performance can be tough. Engineers often reflect on these trade-offs when designing switching power supplies.
A switching power supply is an essential component in many electronic devices. It converts electrical energy efficiently from one voltage level to another. Understanding its key components is crucial for grasping how it works. These components include the transformer, switches, rectifiers, capacitors, and control circuits.
The transformer plays a vital role, allowing for voltage adjustment. According to a report by the International Electrotechnical Commission, transformer efficiency can reach over 95%. However, not all transformers are flawless. Design flaws or poor material choices can lead to energy losses.
Switches and rectifiers contribute to the power supply's efficiency. The switching elements, often transistors or MOSFETs, rapidly turn on and off. This pulsing action helps minimize heat generation. Yet, if not designed correctly, switching losses can occur, affecting performance. Capacitors filter the output and ensure voltage stability. Poorly chosen capacitors can lead to ripple voltage, impacting the overall system reliability. Control circuits manage the operation, but their complexity can lead to increased failure rates if not adequately engineered.
Switching power supplies (SPS) are vital in modern electronics. These devices convert electrical energy with high efficiency. They employ a method called pulse-width modulation (PWM) to control voltage levels. This technique allows optimal energy transfer and reduced waste.
According to a recent report from the International Electrotechnical Commission, SPS can reach efficiencies over 90%. This efficiency minimizes heat generation, making them ideal for compact devices. Additionally, they can adapt voltage levels rapidly, providing stable power across varying load conditions. This flexibility is crucial in applications from consumer electronics to industrial machinery.
However, switching power supplies aren’t perfect. They introduce electrical noise into the system. This noise can interfere with sensitive components. The design of SPS often requires careful consideration to mitigate these effects. Balancing efficiency and power quality is an ongoing challenge for engineers.
Switching power supplies offer numerous advantages that make them a popular choice in various applications. One key benefit is their efficiency. They can convert power with less energy loss compared to linear power supplies. This efficiency translates to less heat generation, which is important in confined spaces. The compact design also allows for smaller electronic devices.
Another significant advantage is their versatility. Switching power supplies can handle a wide range of input voltages. This flexibility makes them ideal for global applications. They can easily adapt to various electrical environments without extensive modification. Additionally, they often feature built-in protections against overloads and short circuits, enhancing overall safety.
However, there are some concerns to consider. Switching power supplies can introduce electrical noise, which might affect sensitive circuits. This noise could lead to operational instability in some devices. It’s vital to assess these potential issues. Moreover, while they are efficient, not all designs achieve the same level of performance. Careful consideration is necessary when selecting the right power supply for your needs. Each design choice carries its own set of trade-offs and complexities.
Switching power supplies are widely used in various applications. They are essential for delivering efficient power to devices. Common uses include computers, televisions, and mobile chargers. These power supplies convert electrical energy efficiently, which reduces waste and heat.
In consumer electronics, switching power supplies ensure devices run smoothly. They adjust voltage levels to meet different requirements. This process is crucial for stability in gadgets. For example, smartphones rely on these supplies to charge quickly without overheating.
Tips: When choosing a power supply, consider its efficiency. An efficient model can save energy and reduce electricity costs. Assess the output voltage and current needs of your devices before making a purchase.
In industrial settings, switching power supplies are vital. They power machines, automation systems, and more. However, not all power supplies are created equal. Some might not provide the required output stability, leading to operational issues. Be sure to test and evaluate before full implementation.
| Application | Description | Voltage Range | Efficiency | Common Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Telecommunications | Used to convert AC mains power to low-voltage DC power. | 48V DC | Up to 90% | Base stations, routers, and switches. |
| Computing | Provides power to computer components such as boards and memory. | 12V, 5V, 3.3V DC | 85% - 95% | Desktop PCs, laptops, and servers. |
| Consumer Electronics | Supplies power to various household electronic devices. | 5V, 12V DC | 80% - 90% | Televisions, gaming consoles, and chargers. |
| Industrial Applications | Controls power in machinery and industrial equipment. | 24V, 48V DC | 90%+ | PLC systems, robotics, and manufacturing equipment. |
| LED Lighting | Drives LED lights by converting AC power into low voltage. | 12V, 24V DC | 85% - 92% | Residential and commercial lighting solutions. |